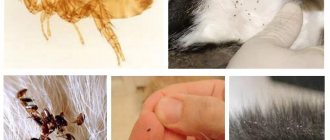
Pediculosis pubis (pubic lice) is a disease caused by the parasite Pthirius pubis, which infects human pubic hair. In addition to the genital area, it can affect other areas covered with hair. It is estimated that this disease affects about 2% of the world's population.
The pubic louse is a small insect about the size of a pin. It is from 1 to 3 mm long and has 6 legs. It is characteristic that her hind legs are thicker than her front legs with large claws. The louse cannot jump and feeds exclusively on blood. Humans are the only known hosts of this parasite. Adults are affected more often than children.
Life cycle of pubic lice
Lice lay eggs most often in the area of coarse hairs in the genital and anal areas of the human body. Less common on the chin, mustache, eyelashes, eyebrows or armpits. They generally don't affect the hair because the hair is much softer than the slightly coarser hair areas above.
The female lays eggs three times a day. The larvae hatch from them after 6-8 days. It takes up to 25 days for the adult stage to form. They feed exclusively on blood 4–5 times a day. Their lifespan is about 30 days.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of lice pubis is not difficult. Firstly, the patient’s complaints with pubic lice are very typical, and secondly, lice or nits themselves are almost always found on underwear or on hair in the area of the body affected by lice. Therefore, the main method for diagnosing pediculosis pubis is to examine the patient. Adult parasites can be seen with the naked eye, but more often a magnifying glass or magnifying glass is used. It is easier to spot the squirrels after they have drunk blood, which gives them a “rusty” coloration.
Symptoms of lice
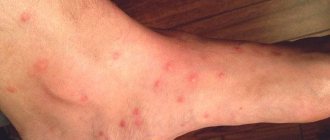
The main symptom of lice pubis is itching in the pubic hair area, which occurs as a result of hypersensitivity to the saliva of the pathogen. It becomes more intense over two or more weeks of infection and occurs more often at night. Characteristic gray-blue spots may sometimes appear in the affected area as a result of the bite. An infected person may see small gray-white insects crawling around or small oval yellow or white lumps (eggs) on the pubic hair.
Routes of infection
Phthiriasis is transmitted sexually. Unlike many other infectious diseases of STD, you can become infected with lice during protected sexual intercourse. However, to establish parasites on the human body, a certain condition is necessary - the presence of hairs.
The fashion for revealing intimate hairstyles has reduced the risk of disease and stopped the scale of the epidemic. Lice are localized on the pubic part if there are hairs. Initially, they cling to the hair, gradually move closer to the skin, push their head under the skin, and practically stick to the body.
Ways of infection by parasites The second way of infection with pubic lice is household. An adult outside the human body lives from 1 day to several months. According to various sources, the louse dies without food within 24 hours. Other sources of information say that under unfavorable environmental conditions, the pubic louse goes into suspended animation and can remain in this state for about two months.
Interesting!
Pubic lice can survive in warm sand. Penetrate to a depth of 1 m from the surface. They detect the approach of a person by smell, instantly come to life, and make their way to the victim. You can become infected with lice pubis while relaxing on the beach.
Infection occurs through contaminated personal items - underwear, towels, dressing gowns, nightgowns and pajamas. However, the most common method is sexual intercourse.
Treatment of pediculosis
Treatment is local, using permethrin preparations or shampoos containing permethrin or lindane. Pregnant women should avoid shampoos containing lindane.
It is imperative to examine and, if necessary, treat the partner, because sexual transmission, despite the use of condoms, is very high, since the condom does not cover the entire genital area where pubic lice may be located.
In addition to treatment, it is recommended to boil and dry towels, clothes and bedding at high temperatures. Abstinence from sexual intercourse is advisable for 24 hours after treatment.
Causes
Most often, pubic louse is transmitted through sexual contact, contact with the skin of a sick person during sexual intercourse, and can also be transmitted through the use of shared clothing, bed, baths, showers. If sexual infestation occurs, lice most often settle on the pubic area, perineum, and around the anus. At home - on chest hair, axillary area, eyelashes. Cases of phthiriasis on the scalp have also been described in children. But this is all conditional: if the disease is not treated, then the reproduction and migration of pubic lice throughout the body is possible. When using a shared towel or bed, it is possible that lice will settle on the pubic area.
Where do they come from and how are they transmitted?
The main route of infection with phthiriasis is sexual. Lice can spread from a sick person to a healthy person through close contact. Moreover, no personal protective equipment will save you from parasites. It is better to have one sexual partner, then the risk of contracting lice pubis will be minimal.
It is also possible to become infected with phthiriasis through household means . This can happen in a sauna, swimming pool, bathhouse, or on the beach. There is a high risk of catching the disease in a hotel or train if the bed linen and towels are poorly washed there. The disease can also be transmitted through other people's clothes, so you need to wear only your own things. If you dry yourself with a towel from an infected person, you can also get sick.
The following categories of people are most susceptible to infection with lice pubis:
- prison inmates;
- homeless people;
- employees of laundries, saunas, baths;
- train conductors;
- military personnel living in barracks;
- tramps;
- women of easy virtue.
REFERENCE! Phthiriasis is transmitted through household means even to children. Lice can be found on their eyelashes and eyebrows.
Danger and possible consequences of infection
Pediculosis pubis is a dangerous disease and very contagious. If it is not treated on time, serious consequences will arise. Constantly scratching the skin due to severe itching can lead to dermatitis or eczema. In addition, the damaged surface is a favorable environment for the penetration of various infections. The occurrence of boils, ulcers, and abscesses cannot be ruled out. In severe cases, even inflammation of the lymph nodes is possible.
A sick person experiences constant discomfort and is unable to get a good night's sleep due to the bites of the squash. Subsequently, he begins to suffer from headaches, neuroses, and depression. Problems arise with the cardiovascular system and other internal organs. There may be an increase in body temperature and loss of appetite.
Parasite bites provoke allergic reactions in the body . If eyelashes or eyebrows are damaged by insects, blepharitis develops. The occurrence of conjunctivitis cannot be ruled out.
Pathogen
This is an insect from the suborder of lice. As the name suggests, the main habitat is the human pubic area, but it also develops other territories where it happily parasitizes, but only where the hair has a triangular cross-section, and not round, as on the head.
The structure of these blood-sucking creatures, the way a pubic louse looks, is all subordinated to a single goal - to lead a parasitic lifestyle, cling tightly and suck blood. You can verify this by looking at the photo. It is very tiny - about two millimeters, almost flat, inconspicuous in color, trapezoidal in shape.
On the head there are mouthparts, the upper jaw and lower lip in which are intended for piercing the skin. The proboscis extends between them. After saturation, they are removed into the cavity. There are hooks around the mouth opening, thanks to which fixation occurs.
Three pairs of legs, the nails of which are screw-shaped, provide hair gripping. The parasite causes a disease known as lice pubis or phthiriasis.
Professional preparations
Treatment of phthiriasis Produced in the form of shampoo, spray, ointment, lotion, cream, emulsion. Each one comes with instructions for use. The purpose of treatment is to apply the drug to the skin, leave it to act for the time specified in the instructions, and rinse off. Re-treat after 10-14 days.
- Spray Pax. The combined drug is applied to the pubis, genitals, and anal area. Leave for 30 minutes. The drug kills pubic lice and soothes the skin after bites. To get rid of pediculosis, 1 treatment is enough. There are enough funds to treat 2 people.
- Nittifor solution. Apply undiluted to hairs and leave for 40 minutes. Wash off thoroughly with water. Repeat the procedure after 10 days.
- Shampoo Pedilin. This easy-to-use product can be used against pubic lice once. The hairs are shaved off and foam is applied to the skin in the perineum and genital area. After 5 minutes, wash off.
The list of remedies for pubic lice is extremely long; the following drugs are also effective:
- Nuda spray;
- Para Plus;
- Nyx cream;
- Veda shampoo;
- emulsion Benzyl benzoate;
- Medifox;
- Hygia.
But it is more convenient to get rid of hairs, disinfect the skin, and carry out therapy aimed at eliminating bites. Without special treatment, pubic lice marks disappear within a week. It is allowed to use Zvezdochka balm, calendula tincture, Bepanten. Female lice pubis should be treated in the same way as male lice.
If an allergic reaction develops against the background of bites, the use of antihistamines and external antiallergic agents is required. But the drugs must be prescribed by a specialist.
Prevention
Based on the fact that any ailment is easier to prevent than to treat, take preventive measures:
- Be picky about sexual intercourse;
- Use only personal items (combs, washcloths, towels);
- Take a bath and wash your clothes more often;
- Shave your pubic area.
Conclusion
It is worth thinking about your safety, since almost 8% of residents of large Russian cities are infected. And in European countries, this disease is becoming an epidemic among the young population.
It's unpleasant to think that dozens of these little parasites will feed at your expense. But if you assume that this is only for people from disadvantaged backgrounds, then you are wrong. Every person should know about the manifestations of lice pubis in order to promptly notice manifestations of the disease in themselves or in their family members.
Pubic lice symptoms in women
The disease (both in women and men) begins with an incubation period, during which there are no signs yet, but the lesions are already on the body. Often incubation lasts no longer than a month.
As soon as this period ends, several signs of the disease appear, the most characteristic of which is severe itching in the pubic area.
What is important is that in some cases the itching spreads to neighboring areas of the body where there is hair (although in women there are not so many such areas). The severity of itching varies: sometimes the patient does not even feel it, and sometimes (especially at night) it is unbearable. This leads to the woman scratching the skin, which is why the skin turns red, eczema forms on it, moreover, through this scratching, secondary infectious diseases can enter the body.
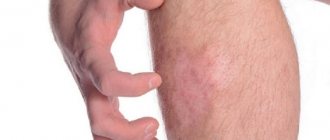
In addition to itching, a symptom of pediculosis is the appearance of shadow or blue spots on the skin (their diameter can reach 10 mm), which, however, quickly disappear. They appear due to minor hemorrhages caused by the sucking of blood, or the deposition of secretions from pubic lice.
On a note! Less commonly, the symptoms described above are accompanied by an allergic rash.
Dark spots may appear on underwear, which are nothing more than waste products of the flats. Finally, a clear sign of the disease is the discovery of lice and their larvae on the skin or underwear. The fact is that parasites, having had their fill of blood, become more noticeable, because their color takes on a “rust” shade.
Who suffers from lice pubis
The previously described parasites received much more attention, mainly due to the fact that they were carriers of typhus from one person to another. But today the appearance of typhus in most developed countries is almost impossible, therefore, pediculosis is no longer considered something terrible. Although there is certainly nothing pleasant about the fact that flats will live on the skin. Many people believe that lice appear only in conditions of extreme unsanitary conditions, but this is not at all true - no one is immune from the disease, a woman can get it even while pregnant.
The cause of the disease is infection from a parasite carrier. Infection itself can occur not only during intimate intimacy, but also in a swimming pool, bathhouse, train or any other public place.
How dangerous is Phthirus pubis?
Fortunately, these insects are not carriers of dangerous diseases, unlike the body and head varieties. But any bites cannot pass without a trace. The consequences appear as:
- Itching and bite marks;
- A bluish spot at the site of the bite.
Interesting! The appearance of a blue spot is associated with the breakdown of hemoglobin under the influence of saliva. The blue color is characteristic of decay products concentrated at the site of the bite.
- Since the bites are scratched, many papules and pustular inflammations form in their place. And if the case is advanced, then pyoderma occurs.
- If eyelashes and eyebrows are affected, blepharitis and conjunctivitis may develop.
Pubic lice, unlike their relatives head and body lice, have a more crab-like structure.
RESULTS
RESULTS ½Ð¾Ð¹ ÑимпÑомаÑикой. RESULTS ROOM °Ð½Ð¸Ñ. RESULTS ½Ñй зÑд в лобковой ÑаÑи.
RESULTS, RESULTS, RESULTS:
- веÑÑние конеÑноÑÑи;
- ÑÑловиÑе;
- бедÑа.
RESULTS › . RESULTS ваÑÑ Ð½Ð° вÑей лобковой повеÑÑноÑÑи.